END TERM EXAM - INFORMATION SECURITY (2017)
Q1 Attempt all the following questions briefly:
(a) What is the difference between threat, vulnerability and risk?
(a) The difference between threat, vulnerability, and risk can be described as follows:
Threat: A potential danger to a system or an asset, such as a malicious act or natural disaster.
Vulnerability: A weakness in a system or an asset that can be exploited by a threat, such as a software bug or a misconfiguration.
Risk: The probability and impact of a threat exploiting a vulnerability, such as a data breach or a system failure.
(b) Describe the major security challenges in laptop and mobile devices.
(b) The major security challenges in laptop and mobile devices include:
Physical theft or loss of the device.
Malware infections through malicious apps, phishing attacks, or software vulnerabilities.
Weak or reused passwords, and lack of two-factor authentication.
Public Wi-Fi security risks.
Social engineering attacks.
(c) What are the various ethical issue framework in information security?
(c) The various ethical issue frameworks in information security include:
Consequentialist: Focuses on the outcomes and consequences of an action, such as the harm or benefit to society.
Deontological: Emphasizes the ethical duties and obligations of an individual, such as respecting privacy or confidentiality.
Virtue-based: Considers the personal and professional virtues and values of an individual, such as honesty, integrity, and accountability.
(d) What is VPN and major security concerns in VPN?
(d) VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, which is a secure and encrypted connection between two or more devices over the internet. The major security concerns in VPN include:
Weak encryption or protocols that can be easily compromised.
Lack of end-to-end encryption, which can expose data to unauthorized access.
Malicious VPN providers that log or sell user data.
Security vulnerabilities in VPN software.
(e) Explain the following attacks: Pharming, packet-spoofing, and zombie attack.
(e) The following attacks can be described as:
Pharming: A type of attack where a malicious actor redirects users to a fake website that looks like a legitimate one, in order to steal sensitive information.
Packet-spoofing: A type of attack where an attacker sends fake packets to a network in order to impersonate a legitimate user, intercept traffic, or launch other attacks.
Zombie attack: A type of attack where a group of compromised computers or devices, also known as a botnet, is used to launch coordinated attacks on a target.
(f) What is media forensics? How ethical hacking different from cracking?
(f) Media forensics is the scientific analysis and examination of multimedia data, such as images, videos, and audio recordings, for evidence and authenticity. Ethical hacking is a legal and authorized process of testing and evaluating the security of a system or network, while cracking is an illegal and malicious activity of breaking into a system or network to cause harm or gain unauthorized access.
(g) Justify with a real time example how authentication can be achieved in banking sector.
(g) Authentication in the banking sector can be achieved through various methods, such as:
Passwords and PINs.
Two-factor authentication, such as using a security token or a biometric identifier.
Multi-factor authentication, such as combining something the user knows (password), something the user has (security token), and something the user is (biometric identifier).
Transaction verification, such as sending a one-time password to the user's registered mobile number or email address.
2 (a) Explain Distributed Information System & it's importance.
Distributed Information System (DIS) is a computer network system where distributed and autonomous computers work together as a single system to achieve common goals. DIS plays an important role in modern information technology as it allows for efficient and effective data management, processing and distribution, and enables organizations to share data and resources across multiple locations. DIS is essential for the success of applications such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). By distributing the workload among multiple machines, a DIS can provide better performance, fault-tolerance, and scalability.
(b) Explain the types of attacks and classification of threat in detail.
Types of attacks on computer systems include malware attacks, denial-of-service attacks, phishing attacks, and social engineering attacks. Malware attacks include viruses, worms, and Trojan horses that exploit vulnerabilities in the system. Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks are designed to disrupt normal traffic and prevent users from accessing a network or website. Phishing attacks attempt to steal sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details. Social engineering attacks use deception to trick people into divulging confidential information.
The classification of threats in information security is done based on the following categories:
Internal and External Threats: Internal threats come from within the organization, such as employees, contractors, or partners. External threats come from outside the organization, such as hackers or cybercriminals.
Active and Passive Threats: Active threats are those that attempt to modify, damage, or steal data. Passive threats are those that attempt to monitor or eavesdrop on data traffic without altering it.
Human and Non-human Threats: Human threats are those that are caused by human error or intentional malicious behavior. Non-human threats are those that arise from natural disasters, hardware or software failure, or other non-human causes.
Intentional and Unintentional Threats: Intentional threats are those that are carried out with the intention of causing harm. Unintentional threats are those that arise due to a lack of security awareness or training.
Understanding the types and classification of threats is critical in developing a comprehensive and effective information security strategy.
Q How biometric system help in securing the information? What are the various criteria's for biometric selection and also explain, how the design issues in biometric systems can be handled taking a case study of any biometric system you have used?
Biometric systems help in securing the information by identifying and verifying an individual based on their unique physical or behavioral traits such as fingerprint, iris, face, voice, signature, and gait. Biometric systems are more secure than traditional authentication methods because they cannot be easily replicated, shared, or stolen.
The selection of a biometric system depends on various criteria such as accuracy, universality, uniqueness, permanence, collectability, and acceptability. The system should be accurate enough to distinguish between individuals, applicable to all people, permanent throughout an individual's life, collectible without causing discomfort, and acceptable to individuals who use it.
Design issues in biometric systems can be handled by considering the usability, privacy, security, and cost factors. Usability issues such as ease of use, speed, and accuracy can be addressed by providing user-friendly interfaces, fast processing times, and high recognition rates. Privacy concerns can be mitigated by implementing data protection measures, such as data encryption, secure data storage, and access control. Security concerns can be addressed by implementing multi-factor authentication, such as combining biometrics with passwords or smart cards. Cost issues can be mitigated by using open-source software, cloud-based solutions, or outsourcing biometric services to third-party providers.
A case study of a biometric system that I have used is the fingerprint recognition system on my mobile phone. The system uses a capacitive fingerprint sensor that captures the unique ridges and valleys on my fingerprint to authenticate my identity. The system has been designed to be user-friendly and fast, and it has a high recognition rate, making it easy for me to access my phone quickly and securely. The system also protects my fingerprint data by encrypting it and storing it securely on the device, ensuring my privacy and security.
Q What is EDI and list the benefits which EDI offers to a business organization? Explain the various components of EDI. How electronic payment system is more beneficial in comparison to traditional payment system?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a technology used for exchanging business documents and information electronically between two or more organizations. It allows businesses to transmit data and documents like purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, etc., in a standardized electronic format without the need for manual data entry.
Some of the benefits of EDI for a business organization include:
Cost Reduction: EDI helps to reduce costs associated with paper-based transactions, including printing, mailing, and data entry.
Increased Speed: EDI allows for faster communication and processing times, enabling businesses to operate more efficiently.
Improved Accuracy: Since EDI eliminates the need for manual data entry, it reduces the chances of errors and discrepancies that can occur in paper-based transactions.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster, more accurate transactions lead to better customer service and increased customer satisfaction.
The various components of EDI include:
Translator: Software that converts data from the company's internal format to the EDI format and vice versa.
Communications: The method of transmitting data between the sender and receiver, which can be through the internet, value-added networks, or direct point-to-point connections.
Standards: Standard formats used for exchanging documents, including X12, EDIFACT, and TRADACOMS.
EDI Applications: Applications that support the process of creating and transmitting EDI documents.
Electronic payment systems are more beneficial than traditional payment systems in many ways. They offer:
Convenience: Electronic payments can be made from anywhere, at any time, and with a few clicks on a computer or mobile device.
Speed: Electronic payments are processed almost instantly, unlike traditional payment methods like checks or money orders that can take days or even weeks to clear.
Lower Costs: Electronic payments are often less expensive than traditional payment methods, with lower processing fees and reduced paperwork.
Security: Electronic payments are more secure than traditional payment methods, as they use encryption and other security measures to protect sensitive information.
Overall, EDI and electronic payment systems are important technologies for businesses, helping them to save time and money, reduce errors, and improve customer satisfaction.
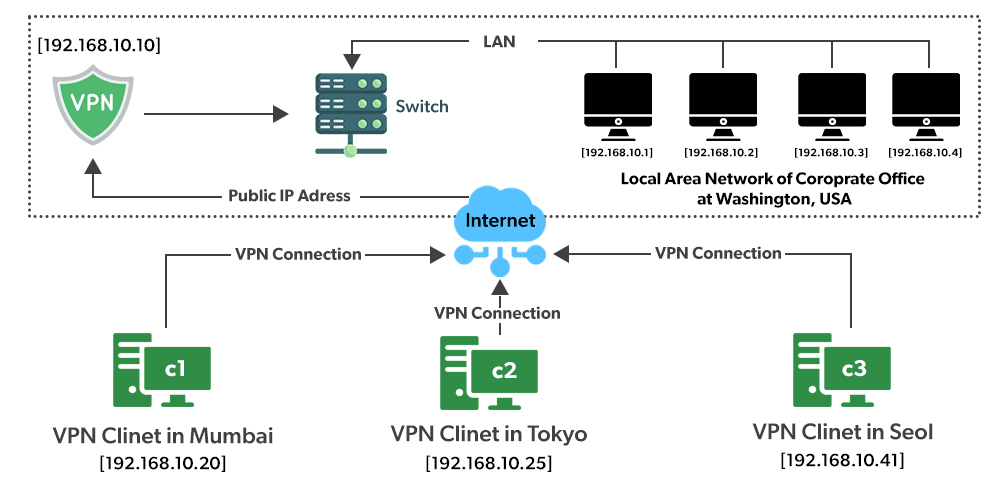
Q What is VPN? List the various protocols of VPN? Also explain in detail, the working of VPN for exchanging information between two private networks with the help of a diagram.
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It is a secure and private network that allows users to access and exchange data over the public internet as if they were directly connected to a private network. VPNs use various protocols and encryption techniques to ensure the privacy and security of the data being transmitted.
Some of the most commonly used VPN protocols include:
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security)
SSL/TLS (Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security)
The working of VPN can be explained using the following diagram:
(source : gfg)
When a user tries to access a private network using a VPN, the following steps occur:
- The user establishes a connection with the VPN server over the public internet.
- The VPN server authenticates the user and establishes a secure connection with the user's device.
- The user's device encrypts all the data being transmitted and sends it to the VPN server.
- The VPN server decrypts the data and routes it to the appropriate private network.
- The data is encrypted again and sent back to the user's device through the VPN server.
- The user's device decrypts the data and presents it to the user.
This way, the data transmitted between the user's device and the private network is encrypted and secure, even though it is being transmitted over the public internet. VPNs provide an added layer of security and privacy to the data transmitted over the internet, making them useful for remote workers, travelers, and businesses with multiple locations.
Q Compare and contrast between IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention System). What are the various intrusion detection methodologies? Also explain any three types of threats.
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) are two security mechanisms used to protect computer networks from various cyber attacks. The main difference between IDS and IPS is that IDS detects intrusions and alerts the security team, while IPS detects and prevents intrusions from occurring in the first place.
IDS works by monitoring network traffic and comparing it to a set of predefined rules or signatures to identify suspicious activity. Once an intrusion is detected, an alert is generated and sent to the security team. IDS can be either network-based or host-based.
IPS, on the other hand, not only detects but also prevents attacks by blocking traffic that violates the predefined rules. IPS is installed inline with network traffic, and it automatically takes action to block the traffic if it identifies an intrusion.
There are various methodologies for intrusion detection such as signature-based, anomaly-based, and hybrid-based.
Signature-based IDS: This methodology is used to detect known attacks based on a signature database of known attack patterns.
Anomaly-based IDS: This methodology is used to detect unusual or abnormal behavior in the network that may indicate an attack.
Hybrid-based IDS: This methodology uses both signature-based and anomaly-based techniques to provide better detection and reduce false positives.
Some common types of threats that IDS and IPS can help protect against include:
Malware: Malicious software such as viruses, worms, and Trojans can infect a computer or network and cause damage.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks: Attackers flood a network or website with traffic to make it unavailable to users.
SQL injection attacks: Attackers inject malicious code into a website's SQL database to steal data or compromise the website.
In summary, IDS and IPS are two important security mechanisms that help protect networks from cyber threats. IDS detects intrusions and alerts the security team, while IPS detects and prevents intrusions from occurring. The selection of a methodology depends on the requirements of the organization, and each has its own strengths and weaknesses.
Q Distinguish between Symmetric and Asymmetric key cryptography. Which type of cryptography is more secure and why? Explain the Diffie- Hellman Key Exchange algorithm for symmetric key cryptography.
Symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography are two popular methods of encrypting information.
Symmetric key cryptography involves the use of a single secret key for both encryption and decryption of data. The same key is shared between the sender and receiver of the data. The major advantage of this method is its speed and efficiency, but the key must be kept secret to prevent unauthorized access.
Asymmetric key cryptography involves the use of two separate keys for encryption and decryption of data. One key, the public key, is made available to anyone who wants to send encrypted messages. The other key, the private key, is kept secret and is used to decrypt messages. The main advantage of this method is its enhanced security, but it is slower and less efficient than symmetric key cryptography.
In terms of security, asymmetric key cryptography is considered more secure than symmetric key cryptography because the private key is never shared with anyone. This eliminates the risk of a third party intercepting the key and accessing the data. However, it is computationally more expensive than symmetric key cryptography.
The Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm is a popular method for exchanging symmetric keys in a secure manner. It involves the use of a mathematical algorithm to create a shared secret key between two parties. The shared key is then used for symmetric key cryptography.
In the Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm, two parties agree on a large prime number and a base number. Each party then selects a secret number and calculates a public value based on the prime number, the base number, and the secret number. The two parties then exchange their public values and calculate a shared secret value using their own secret value and the other party's public value. The shared secret value is then used as the symmetric key for encryption and decryption of data.
In summary, both symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography have their own advantages and disadvantages. While symmetric key cryptography is faster and more efficient, asymmetric key cryptography is considered more secure. The Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm is a popular method for securely exchanging symmetric keys in a two-party communication.
Q Write a short note on the following:
(a) Business Transaction on Web.
Business transactions on the web refer to the activities or exchanges that occur between two or more parties through the use of the internet. The web has revolutionized the way businesses conduct transactions and communicate with their customers. Today, customers can shop online, pay bills, transfer money, and interact with businesses from anywhere in the world.
Some of the advantages of business transactions on the web include increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved customer service, and access to a larger customer base. However, businesses must also be aware of the risks involved in conducting transactions on the web, such as identity theft, fraud, and cyber attacks. To minimize these risks, businesses must implement adequate security measures and follow best practices in web transaction management.
(b) Legal challenges framework for Information Security.
Information security is a critical aspect of modern business operations, and organizations face numerous legal challenges in ensuring the protection of sensitive data and information. These legal challenges include complying with various regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, and dealing with legal issues related to data breaches, cyber attacks, and other security incidents.
To overcome these legal challenges, businesses must implement effective security policies and procedures, conduct regular risk assessments, and ensure that their security measures are in compliance with relevant regulations and standards. Businesses must also have a plan in place to deal with security incidents, such as a data breach or cyber attack, and be prepared to respond quickly and effectively to mitigate any damage. Additionally, businesses should work closely with legal experts to ensure that their security measures are in compliance with relevant laws and regulations and to handle any legal issues that may arise.




Comments
Post a Comment